10 Most Common Diseases In Malaysia

It's the natural order of things: as human beings, we get sick every once in a while. But due to certain factors such as lifestyle, personal habits and our environment just to name a few, certain diseases are more prevalent than others. While you may know of "killer" diseases such as cardiovascular diseases, cancer, diabetes, stroke and such, this article highlights 10 most common diseases in Malaysia which are infectious. Without further ado, check them out and learn how to prevent them!
What Are The Most Common Diseases In Malaysia?
1) Food Poisoning
Food poisoning, otherwise known as foodborne illness, is caused by consuming contaminated food. In most cases, food poisoning is usually not severe, though some people may need to be hospitalised. Even without treatment, most people usually recover from food poisoning within a few days. The food in question can be contaminated at any point during production, processing or cooking. Unsanitary handling, unsuitable storage and unthorough cooking are just a few ways food can get contaminated by bacteria, virus or even parasites.
Symptoms: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, stomach cramps, abdominal pain, lack of energy, loss of appetite, fever, muscle aches
Prevention:
- Wash and clean food, utensils and food surfaces regularly, thoroughly and properly
- Separate raw foods from ready-to-eat/cooked foods to avoid cross-contamination
- Cook food properly at a suitable (high) temperature
- Store food at a suitable temperature (refrigerate or freeze)
- Defrost food in the refrigerator unless you plan on cooking it immediately
- Throw expired or questionable food away

2) Leptospirosis
Leptospirosis might not sound it, but apparently it's still one of the most common diseases in Malaysia. Affecting both humans and animals, it is a bacterial disease most commonly transmitted from animals to humans via open wounds, the eyes or mucuous membranes. It actually has a wide range of symptoms, which could be mistaken for other diseases, or it can be asymptomatic as well. Without treatment, it could lead to other complications and diseases including kidney damage, miningitis, liver failure and even death. Outdoor or agricultural workers are most at risk since they are constantly being exposed to possible contaminated water/soil, but leptospirosis can spread through recreational activities as well, such as water sports, canoeing or white-water rafting--anywhere that could have a possible contamination by animal urine. Floods facilitate the spread of leptospirosis as it is highly likely that flood water is contaminated.
Symptoms: High fever, headaches, chills, muscle aches, jaundice, red eyes, diarrhoea, vomiting, abdominal pain, rashes
Prevention:
- Wearing protective clothing for those who are at risk
- Avoid from swimming/wading in possible contaminated water
- Rodent control
- Vaccination
- Cover up cuts with waterproof dressing if going into bodies of water
- Drink clean water
- Avoid consuming anything that has been in contact with flood water

3) Gonorrhoea
Gonorrhoea is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections (STIs), and sometimes it doesn't even have symptoms, so people don't even know they've contracted gonorrhoea. It is usually passed on through unprotected vaginal, anal and/or oral sex (or even just close genital contact), though a pregnant mother could also pass on the infection to her baby at birth. Gonorrhoea is curable, but if it is left untreated it can also spread to other parts of the body, and could even cause infertility. You can't contract gonorrhoea through kissing, hugging, sharing towels or using the same toilet as one who is infected.
Symptoms for men: Unusual discharge (which may be green, yellow or white), pain or burning while urinating, inflammation or swelling in the foreskin, pain or swelling in the testicles, greater frequency or urgency of urination.
Symptoms for women: Unusual discharge (which may be thick and green or yellow), pain or burning while urination, abdominal or pelvic pain, bleeding in between periods or heavier periods, bleeding after sex, greater frequency or urgency of urination, general vaginal irritation, fever.
Prevention:
- Use protection e.g. condoms
- Wash sex toys after use, or cover with a new condom every time before use
- Avoid sharing sex toys
- Consider regular screening for both you and your partner
- Limit your number of sex partners
- Get tested before you and your (new) partner have sexual intercourse

4) Dengue Fever
Unfortunately, Malaysia is no stranger to dengue fever. Spread by the Aedes mosquito, characterised by its trademark black-and-white striped legs and body, dengue fever is considered common, but it can lead to serious complications. In fact, it is one of the leading causes of serious illness and death in certain countries. There are four serotypes of the dengue virus, called DENV. That means that it is possible to be infected four times in a person's lifetime. There is no specific treatment for dengue fever as yet, but early detection is key to avoid complications. Sometimes symptoms may be mild and mistaken for other sorts of illnesses or a flu, so it's best to get tested if you think you might have it.
Symptoms: High fever, severe headaches, pain behind the eyes, muscle aches, joint pain, rashes, nausea, fatigue, vomiting, mild bleeding (from nose or gums), easy bruising, swollen glands.
Prevention:
- Minimise mosquito breeding grounds (stagnant bodies of water)
- Apply mosquito/insect repellent
- Use mosquito nets
- Keep windows closed as much as possible
- Wear long-sleeved clothing

5) Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is the most common serious liver infection in the world, and it is a potentially life-threatening one. However, there's some good news: if you contract it as an adult, your body should be able to fight it off, and then you'll be immune for the rest of your life. But also, if you're unlucky, it can cause scarring of the liver, liver failure and even liver cancer. One can get infected through sex and sharing of needles, and pregnant women can pass on the infection to their baby at birth as well. Babies who are born with Hepatitis B is likely to remain infected for a lifetime. Newly-infected individuals may not show any symptoms, but a simple blood test will reveal results.
Symptoms: Jaudice, dark urine, light-coloured stool, fever, long-term fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, belly pain, loose stool, muscle aches, constipation.
Prevention:
- Vaccination
- Practice safe sex
- Wear gloves if you have to clean up after others (especially if you need to touch bandages and linens etc.)
6) HIV
HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) is a type of virus that attacks cells that help the body fight against infection, making the person more susceptible and vulnerable to other infections and illnesses. To date, HIV still remains uncurable, and the body can't rid itself of HIV, meaning that HIV is a lifetime condition. However, that's not to say that all hope is lost. HIV can be treated and controlled, so that those infected could still live a long and healthy life without transmitting the virus on to other people. Primarily, it is transmitted through bodily fluids, including blood, semen, vaginal and rectal fluids. It doesn't spread through air or water. If left untreated, HIV can progress to AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome).
Symptoms (Acute stage): Fever, chills, rashes, sore throat, muscle aches, fatigue, swollen lymph nodes, diarrhoea, nausea, vomiting, night sweats, ulcers.
Prevention:
- Practice safe sex, or abstinence
- Avoid from sharing needles
- HIV-prevention medicine

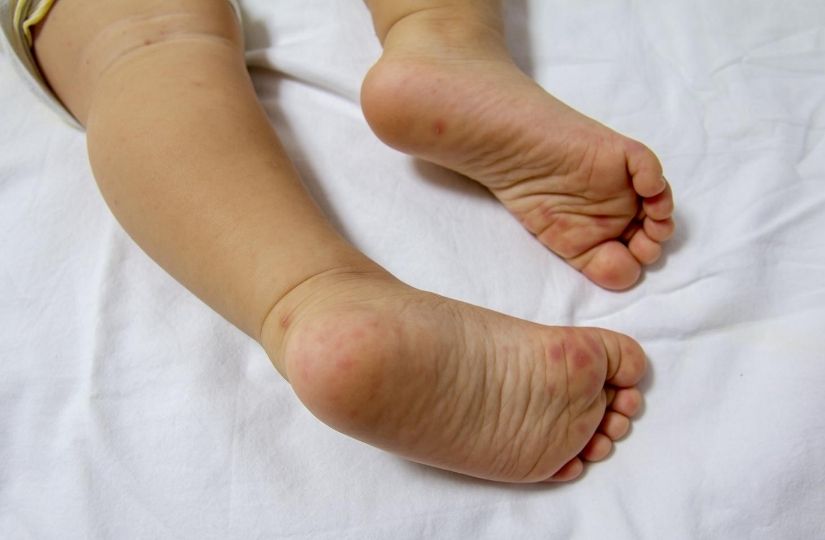
7) Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease
Hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD) is common in young children, especially those under the age of 5, though anyone can get it. It's not considered serious, but it is highly contagious, especially in kindergartens and daycare centres, where it can spread like wildfire. Transmission occurs through saliva, mucus, fluids from injuries, stool and unwashed hands or surfaces. It causes painful mouth ulcers, and rashes or blisters on the hands/arms, legs/feet and/or butt. As it is caused by a virus, there's no medicine to cure it, but it usually resolves within a week or two.
Symptoms: Ulcers, rashes/blisters, sore throat, loss of appetite, fever, general discomfort, irritability, fatigue, headache.
Prevention:
- Practice good hygiene e.g. wash hands often
- Wipe down and disinfect surfaces
- Avoid close contact with the sick
8) Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis, or most commonly known as TB is a bacteria that usually affects the lungs, but it can also attack other body parts such as the kidney, spine and brain. What's curious about TB is that not everyone infected with the TB bacteria will become sick, and TB is divided into latent TB and active TB. With latent TB, the germs are present in you body, but they are not "activated" and therefore will not cause you to be sick or transmit the disease. Active TB is well, active, and risk of transmission is there. If left untreated, TB can be fatal. In fact, TB is one of the top 10 causes of death worldwide. That said, TB is curable with antibiotics, though you'd have to keep taking them for 6-9 months. Just like colds or flus, TB is spread through the air.
Symptoms: Cough that lasts for 3 weeks or more, chest pain, coughing up blood or sputum, weakness, fatigue, weight loss, loss of appetite, chills, night sweats, fever
Prevention:
- For latent TB, ensure that you take medication so that it doesn't become active and contagious
- Avoid crowds, especially in countries/places where TB is common
- Vaccination

9) Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a viral infection that causes liver inflammation, and can lead to serious liver damage. It is also one of the major causes of liver cancer. Sometimes "silent", many do not know that they have Hepatitis C till serious damage has occurred. However, chronic Hepatitis C is still curable with oral medication taken everyday for 2-6 months. At the moment, no vaccine is effective against Hepatitis C, though research is still ongoing. Hepatitis C is a bloodborne virus, so those who are exposed to contaminated blood are at risk of contracting Hepatitis C, and a pregnant mother could also pass it down to her child at birth.
Symptoms: Bleeding/bruising easily, fatigue, jaundice, dark-coloured urine, loss of appetite, itchy skin, fever, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, grey-coloured stool, joint pain, fluid buildup in abdomen.
Prevention:
- Practice safe sex
- Wear gloves if you have to clean up after others (particularly if it involves blood)
- Be cautious about piercings/tattoos and their equipment
10) Malaria
Another one of those diseases that is caused by mosquitoes, malaria is caused by parasites that are transmitted to humans through infected Anopheles mosquitoes. If left untreated, it could be life-threatening, though it is also preventable and curable. Children under the age of 5 are most vulnerable. Once an infected mosquito bites a person, the parasites are transmitted to the human. The parasites make their way to the liver, where they mature. The mature parasites then enter the bloodstream and start infecting red blood cells. Since malaria is transmitted by blood, it can also be trasmitted through organ transplants, blood transfusion and shared needles or syringes. Pregnant mothers can also pass down malaria to her child at birth.
Symptoms: Fever, headache, chills, severe anaemia, respiratory difficulties, multi-organ failure, sweating, nausea, vomiting, convulsions, muscle aches, bloody stool.
Prevention:
- Mosquito nets (can be insecticide-treated)
- Spraying/fogging
- Taking certain medication
- Apply insect repellent
- Wear long-sleeved clothing
- Destroy mosquito breeding grounds

This is but a brief overview of some of the most common diseases in Malaysia, but if you're in doubt or are feeling unwell, it's best to seek professional help! Nowadays, you don't even have to step out of your house for consultation anymore! Simply check out some of these Best Telemedicine Apps in Malaysia, and you can speak to doctors and even get medication delivered to your doorsteps!











































